UVM Class Hierarchy
UVM classes have 3 major types
- UVM object
- UVM transaction
- UVM component
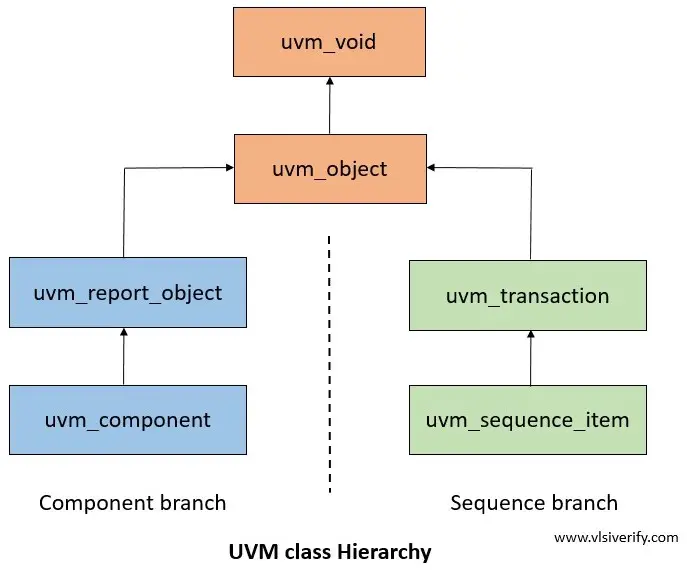
As shown in the above diagram,
uvm_object is derived from the uvm_void class. Further component and sequence branches are inherited from the uvm_object class.
uvm_void
The uvm_void is the base class for all the UVM classes. It is an abstract class that does not have any data members or methods implemented. It is a generic container for objects to be created similar to void pointer in C language.
Syntax:
virtual class uvm_voiduvm_object
The UVM object is a data structure used for testbench configuration and it is the base class available for component and sequence branch. The uvm_object provides methods like create, clone, copy, record, compare, print, etc.
uvm_report_object
The uvm_report_object provides reporting functionality for UVM. The message, error, or warning prints are very important for debugging purposes that are being facilitated by the uvm_report_object class.
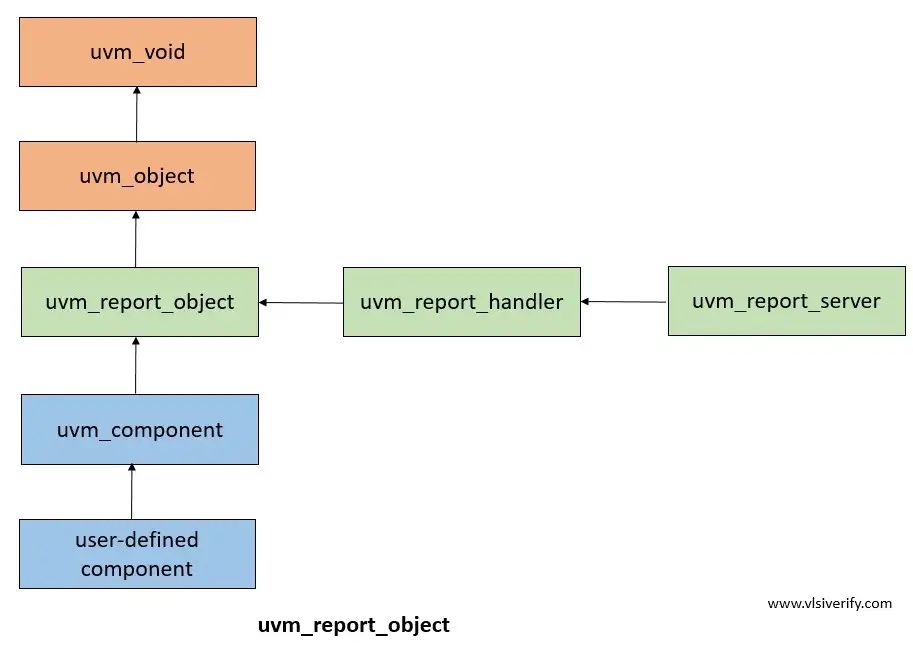
Most of the methods in uvm_report_object are passed to an instance of uvm_report_handler that stores reporting configuration. Based on the configurations, uvm_report_handler decides whether to display the message or not. It is then passed to uvm_report_server for actual formatting and producing the messages. The detailed report has information for id string, verbosity level, severity, and a complete message string.
Report macros: UVM provides a set of macros that are wrappers around uvm_report_* functions as shown below:
|
Macros |
Reporting functions |
|
`uvm_info |
uvm_report_info |
|
`uvm_warning |
uvm_report_warning |
|
`uvm_error |
uvm_report_error |
|
`uvm_fatal |
uvm_report_fatal |
Syntax:
|
Macros |
Syntax |
|
`uvm_info |
`uvm_info(ID,MSG,VERBOSITY) |
|
`uvm_warning |
`uvm_warning(ID,MSG) |
|
`uvm_error |
`uvm_error(ID,MSG) |
|
`uvm_fatal |
`uvm_fatal(ID,MSG) |
Where,
ID: message tag
MSG: A text message
VERBOSITY: If VERBOSITY is lower than configured verbosity for that reporter, it will be printed.
Note: `uvm_warning has UVM_NONE as a default verbosity.
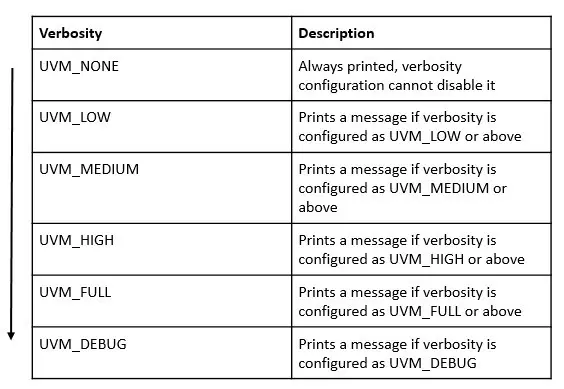
uvm_verbosity
UVM defines standard verbosity for report displays.
UVM Transaction
UVM transaction is used for generating stimulus and its analysis. They are transient in nature The simple transactions can be derived from the uvm_transaction class. But sequence-specific transactions are recommended to derive from uvm_sequence_item.
UVM Components
UVM components are used to build a class-based hierarchical structure for the testbench. The uvm_component are static and physical components that exist throughout the simulation. The uvm_component class is a base class for all UVM components. For testbench hierarchy, base class components are available in UVM as uvm_env, uvm_agent, uvm_monitor, uvm_driver, uvm_sequencer, etc.
The uvm_component provides the following interfaces
Hierarchy
Provides methods for searching and traversing component hierarchy.
Example:
get_parent: It returns a handle for the current component’s parent. If it has no parent, then it returns null.
get_full_name: It returns a complete hierarchical name for this object.
Phasing
Provides standard phase methods and APIs for custom phases. This allows all components to execute in synchronization.
Example: build_phase, connect_phase, run_phase, etc.
Reporting
Provides an interface to uvm_report_handler to process all messages, errors, and warnings.
Example: set_report_id_verbosity_hier, set_report_verbosity_level_hier
Objection
Provides an interface to the uvm_objection mechanism.
Example: raised, dropped, all_dropped, etc.
Configuration
Provides an interface to the configuration database
Example: print_config_settings, print_config, apply_config_settings, etc
Transaction recording
Provides interface to record transactions consumed or produced by the component to a transaction database.
Example: accept_tr, begin_tr, record_error_tr, tr_database, etc.
Factory
Provides an interface to the uvm_factory to create new components and objects. This also allows an override mechanism for components and objects.
Example: create_component, create_object, set_type_override_by_type, set_inst_override_by_type, etc
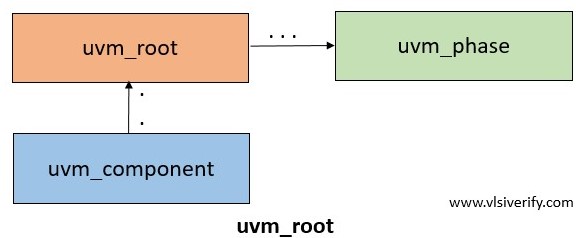
uvm_root
The uvm_root class is an implicit top-level class for all UVM components. It also controls the phase mechanism. The UVM automatically creates a single instance of the uvm_root class that is accessed by the uvm_top variable (global variable having uvm_pkg scope).
- Any component having a parent specified as null becomes a derived class of uvm_top.
- Manages phasing for all components.
- It searches for the component based on its hierarchical name using find and find_all methods.
- It globally configures resort verbosity for the log files.
Example: uvm_top.set_report_verbosity_level_hier (UVM_MEDIUM) - Since uvm_top is globally accessible in uvm_pkg scope, UVM’s reporting mechanism is also accessible from anywhere (even outside of uvm_component) like sequences or objects.
Example: uvm_report_warning, uvm_report_error, etc
Difference between uvm_component and uvm_object
- UVM components are non-transient whereas UVM objects are transients.
- UVM components are static in nature and exist throughout the simulation and UVM objects are dynamic in nature that has a limited lifetime in the simulation.
- `uvm_component_utils and `uvm_object_utils macros are used for factory registration for UVM components and objects respectively. They can not be used interchangeably.
- Default constructor for uvm_component has two arguments: name and parent
Default constructor for uvm_object has a single argument: name
These are hardcoded arguments for the constructor and the user is not allowed to change arguments along with factory usage.
Difference between uvm_object, uvm_transaction and uvm_sequence_item
- The uvm_transaction class is inherited from uvm_object that adds additional information of a timing, notification events, and recording interface.
- The uvm_sequence_item class is derived from the uvm_transaction class that adds basic functionality for sequence and sequence items like get_sequence_id, set_sequencer, get_sequence, etc.
- It is important to note that uvm_transaction usage is deprecated as a base class for user-defined transactions. Hence, the uvm_sequence_item class shall be used as a base class for user-defined transactions.
UVM Tutorials