Tutorials
Learn More
UVM Sequence
UVM sequence is a container that holds data items (uvm_sequence_items) which are sent to the driver via the sequencer.
uvm_sequence hierarchy
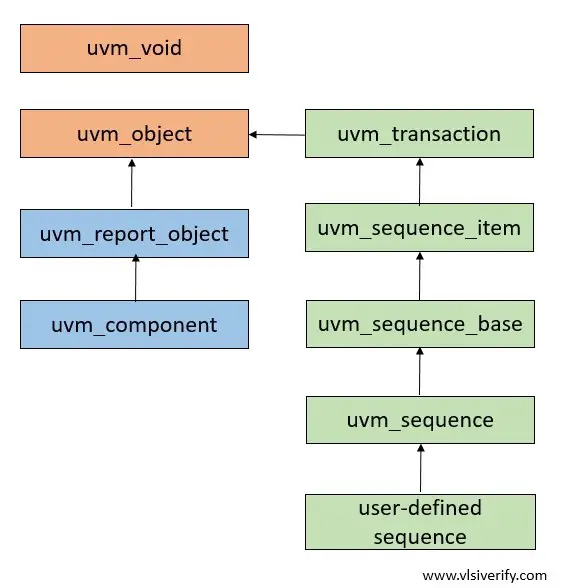
Note: uvm_sequence class is parameterized with uvm_sequence_item.
uvm_sequence class declaration:
virtual class uvm_seqence #( type REQ = uvm_sequence_item, type RSP = REQ) extends uvm_sequence_baseuvm_sequence class structure
class my_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(my_seq_item);
`uvm_object_utils(my_sequence)
function new(string name = "my_sequnce");
super.new(name);
endfunction
task body();
...
endtask
endclassWhy `uvm_object_utils is used in sequence, why `uvm_sequence_utils are not used?
`uvm_sequence_utils is a string-based sequence library that is deprecated in UVM.
What is the body() method?
The operation which is intended to do by sequence is defined inside a body method.
Along with a body() method, pre_body, and post_body methods are called by default.
class my_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(my_seq_item);
`uvm_object_utils(my_sequence)
function new(string name = "my_sequnce");
super.new(name);
endfunction
task pre_body();
...
endtask
task body();
...
endtask
task post_body();
...
endtask
endclassNote:
- These pre_body and post_body tasks are additional (can be named as callbacks) which are useful to perform any operation before and after the execution of the body() method.
- pre_body() and post_body() methods are optional.
How to write a sequence?
An intention is to create a seq_item, randomize it, and then send it to the driver. To perform this operation any one of the following approaches is followed in the sequence.
- Using macros like `uvm_do , `uvm_create, `uvm_send etc
- Using existing methods from the base class
a. Using wait_for_grant(), send_request(), wait_for_item_done() etc
b. Using start_item/finish_item methods.
Let’s discuss the macro-based approach in UVM sequence macro and existing methods approach in the uvm_sequence_base class methods section.
UVM Tutorials